A technical overview of Citrix on Azure Cloud Architecture
Introduction
In application and desktop virtualization, Citrix has been the leader for over two decades. The new version of XenApp, XenDesktop is now ready for Cloud.
Citrix XenApp and XenDesktop provides session, application and desktop virtualization technologies to administrators to manage centralized hosted applications and desktops. Also, it provides advanced management and scalability, a rich multimedia experience over any network and self-service applications with any endpoint devices such as (laptops, smartphones, PCs, tablets and Macs).
Microsoft Azure is a reliable and flexible cloud platform that allows simple as well as multi-tier applications to be deployed quickly in Microsoft-managed data centers. The architectural model presented here describes a basic Azure deployment for delivering Citrix application and desktop services to users. It enables a hybrid approach in which organizations can extend on-premise infrastructure and use Azure IaaS to deliver these services. Key objectives for the design include easy scalability of XenApp and XenDesktop workloads as well as high availability.
Microsoft Azure for Citrix
Microsoft Azure hosts infrastructure components in Microsoft managed datacenters on geographic regions. Which allows to provision or deploy XenApp and XenDesktop on Azure IaaS on demand.
Microsoft Azure deployment consideration
As part of the planning stage when evaluating Hybrid Cloud solutions. One of the considerations for many organization is geographic diversity – both for supporting a global user audience as well as for disaster recovery purposes.
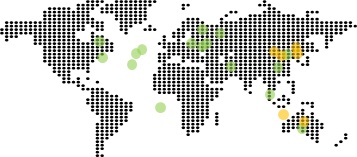
Microsoft Azure Global Footprint
Microsoft Azure deployment concepts
Microsoft Azure makes it possible to spin up new VMs in minutes and adjust usage quickly as infrastructure requirements change and “Pay-as-you-go” pricing for Azure virtual machines. When deploying XenApp or XenDesktop on Azure, there are three critical types of Azure IaaS components: compute, storage, and networking.
- Azure IaaS Components:
1. Compute – Virtual Machines
VMs supply the basic Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) functionality and are assigned compute, memory, and I/O resources based on an Azure compute instance type.
Cloud Services
Azure Cloud Services function as containers for VMs, simplifying deployment and scalability of multi-tier applications.
Availability Sets
Defining VMs in an Availability Set causes them to be hosted on different racks in the Microsoft data center, enhancing availability. As shown in the Microsoft Azure deployment concepts and terminology. Cloud Service on the left contains both VMs as well as VMs defined in an Availability Set (outlined by a red dashed line). The Cloud Service on the right houses multiple VMs. All VMs in a Cloud Service are automatically connected to the same virtual network and permit communication across all UDP and TCP ports.
2. Storage Accounts – Azure provides different storage categories and redundancy options and offers three options for replicating page blob storage for VMs.
Page Blobs
Azure VMs use “page blobs”, block storage that is optimized for random read and write operations and is therefore recommended for XenApp deployments.
i) Local Redundant Storage (LRS), which creates three synchronous data copies within a single data center.
ii) Geographically Redundant (GRS), which replicates data three times in a primary region and three times in a remote secondary region to protect against a data center outage or a disaster.
iii) Read-Access (RA-GRS), which is the same as GRS but supplies read access to the secondary data center.
3. Networking – Azure allows the creation of standalone, cloud-only virtual networks as well as VPNs that support cross-premises connectivity. VMs constructed within an Azure virtual network can communicate directly and securely with one another, and there is no cost associated with VM communication or data transfers within a single region.

Microsoft Azure deployment concepts and terminology
- Citrix Infrastructure Components
In support of a XenApp deployment on Azure, the following additional components are configured or provided by Azure:
- Active Directory (AD)-Client authentication and access management
- DNS–For Name resolution
- DHCP–IP configuration Azure provides DHCP services that assign private IP addresses to VMs using a specified IP address range.
- SQL-Static information and configuration settings store.
- Delivery Controller–to manage XenApp and XenDesktop connections and connection policies, and acquire licenses for end-users.
- StoreFront- enable user log-on and the selection of different desktop and application options.
- Netscaler VPX- encrypt and authenticate all connections between users and the XenApp infrastructure.
- Traffic Manager- for DNS load balancing and route traffic to different virtual networks in different data centers.
Network-level load balancing- Azure can load balance external traffic across virtual machines in a Cloud Service or internally between virtual machines in a Cloud Service or virtual network.
Implementing Citrix XenApp and XenDesktop on Azure IaaS
- Citrix XenApp deployment architecture on premise design.

On Premise XenApp Architecture
- The first step in an Azure implementation is to create a sizing plan based on specific requirements. The appropriate number of Cloud Services, Storage Accounts, and VMs required in Azure depends on estimates for the number and type of users in the environment.
- There are different server functions that must be considered in the sizing of Azure resources: Infrastructure servers, XenApp workload servers, and XenDesktop VDI workload servers. In planning an Azure deployment, it’s necessary to consider the appropriate sizing of each.
- XenApp/XenDesktop infrastructure and workload servers must be co-located in a single Azure region. XenApp and XenDesktop virtual servers can’t be distributed or split across multiple Azure regions (although more than one site can contain a full deployment).
- Implementing Citrix XenApp and XenDesktop on Microsoft Azure IaaS, the deployment architecture follows a traditional on premise design for provisioning XenApp workloads.

-
As in a traditional on-premise XenApp topology, the NetScaler service receives client requests and proxies network traffic to the XenApp/XenDesktop worker hosts in the virtual network. StoreFront servers provide login services and a directory from which users select desktop and application services. Delivery Controllers distribute connections and set up service delivery from XenApp session and XenDesktop VDI hosts.
Advantages
Using Azure as infrastructure for a Citrix-powered desktop and app solution allows customers to grow the environment gradually and predictably without having to over-size a solution for the worst-case load scenarios. Avoid the large capital expense associated with build outs and “pay as you go”
Business continuity to leverage XenDesktop on Windows Azure during business disruptions caused by power outages, natural disasters or other unforeseen disruptions.
References
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/documentation/articles/azure-subscription-service-limits/
http://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/virtual-machines
https://www.citrix.com.pl/solutions/desktop-virtualization/overview.html
http://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/documentation/articles/azure-subscription-service-limits/
About Author
Sameer Asif is a Lead Technical Consultant with 7 years of industry experience as Citrix consultant. Worked on implementation, migration, deployment, up gradation of Citrix XenApp, XenDesktop, PVS and VDI Windows Server family, AD, DNS, DHCP, Group Policy, Xen Server, VMware Esxi4.1 and Microsoft Certified Professional.
 CREATE TABLE mytable
CREATE TABLE mytable



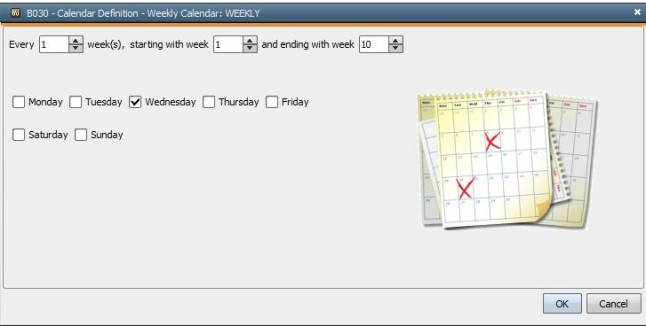
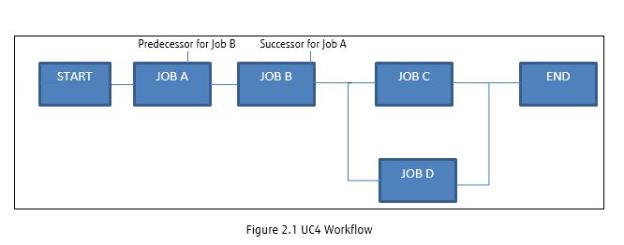 To schedule the workflow to run on every Wednesday, create the weekly calendar keyword in Calendar object.
To schedule the workflow to run on every Wednesday, create the weekly calendar keyword in Calendar object.